Much like other Scandinavian countries, Norway has a sophisticated telecom market with high broadband and mobile penetration rates and a highly developed digital media sector. Although not a member of the European Union, the country’s telecoms sector is synchronised with relevant EC legislation. Telenor is the dominant operator in all sectors, though there is increasing competition from new entrants. Telia Norway increased its market share by acquiring the operations of Tele2, Phonero and Get.
Denmark & Norway frequent on @opensignal's Global Mobile Network Experience Awards 2022. One Swedish entry, no Finnish. We highlighted Nordic operators. https://t.co/yWfc8VnAs9 @TelenorN_presse @TDCNET_DK @iceno_presse @telianorge @3Sverige @3Danmark @TelenorDanmark @TeliaDanmark pic.twitter.com/gBXZ4koWTo
— tefficient 🚥 (@tefficient) February 8, 2022
Norway enjoys near comprehensive LTE coverage, while both Telenor and Telia are looking to close their 3G and 2G networks (by 2020 and 2025 respectively), focussing instead on LTE and 5G technologies. The mobile broadband sector was bolstered by the auction of spectrum in the 700MHz and 21MHz band in June 2019. Additional spectrum in the 700MHz is expected to be auctioned for mobile broadband use (5G) in 2021.
Telia in Norway has switched off 3G completely (in 2100 and 900 MHz) and refarmed the spectrum for 4G. 5G will be available nationwide in 2023 and "2G and 4G will coexist with 5G for a long time to come"#2G #3G #3G4G5G #2G3Gshutdown https://t.co/75coYUQbOt
— Zahid Ghadialy (@zahidtg) November 11, 2021
The broadband penetration rate is among the highest in Europe, while in recent years subscribers have been migrated to faster broadband solutions over fibre networks, VDSL and upgraded cable infrastructure. The leading ISPs Telenor and NextGenTel have also deployed services based on G.fast technology.
The regulator has called on the government to help fund additional cable infrastructure to reduce the country’s dependence on Telenor’s networks. In late 2019 the government proposed making broadband of at least 20Mb/s a universal service.
Norway currently has three mobile networks: Telenor, Telia (formerly NetCom), now merged with Tele2 (by Network Norway) after being acquired by Telia and ice.net (4G/LTE and 5G, no prepaid).
Many public places and public transport are covered by WiFi. For instance, the shuttle bus from Oslo airport to the city centre has free WiFi. Norwegian airline provides free WiFi, many ferries and metro trains as well. So you might not need mobile internet when entering the country.
Populated areas have very good mobile network coverage, even at some remote mountains areas or fjords. The Svalbard archipelago (including its main island Spitsbergen) is covered by all Norwegian providers as well.
The Norwegian providers have shut down their 3G networks in Norway in 2020/21 and plan to re-used the spectrum for their 4G/LTE and 5G networks. From 2021 Norway is on 2G, 4G/LTE and 5G only.
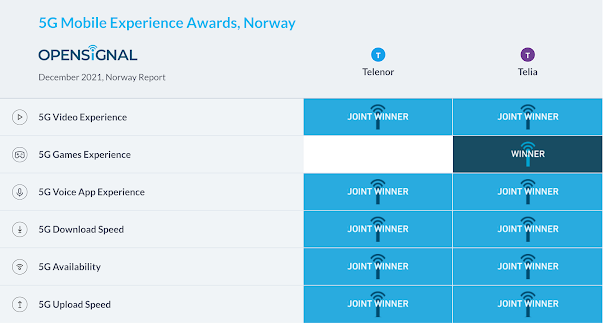
According to the December 2021 OpenSignal report the Norwegian mobile network experience landscape characterized by extreme competition. Out of six awards for the taking, five award categories resulted in a tie between Telenor and Telia, with the remaining one — 5G Games Experience — being the only category featuring an outright winner, Telia. They included the two national operators that had launched 5G commercially before the data collection period — Telenor and Telia — as ICE launched its 5G commercial network afterwards, in November 2021.
Telenor is market leader in Norway with more than 50% of the national users on its network. It has a good coverage and speeds throughout the country: Telenor Coverage map. 4G/LTE is available for prepaid. Starting in 2019 Telenor will gradually shut down their 3G network to be switched off by 2021. For data you need a 4G device now on B3 (1800 MHz), B7 (2600 MHz) or B20 (800 MHz).
Telenor Norway and Ericsson have entered into a joint innovation cooperation to create new 5G-powered opportunities in areas such as entertainment, autonomous transport, smart factories and remote healthcare. According to Ingeborg Øfsthus, CTO of Telenor Norway:
“5G is more than a new network, it is a bridge into the future. 5G will have a strong positive impact on society. Through our innovation collaboration we will pave the way for both services critical for society and commercial services that will drive the digitalization of Norway. Telenor has speeded up our building of the future 5G network in Norway. The full modernization of the mobile network in Norway is an ambitious undertaking, and the new technology will give Norwegians access to products and services that have never before been available. With 5G we get fiber optic speed over the mobile network.”
Telenor Norwary’s 5G network was commercially launched on 13 March 2020. The 5G service was initially launched in Oslo, Bergen, Stavanger and Sandnes.
Telia Norge, formerly called NetCom is Norway's runner up, owned by Swedish Telia Group. After the merger with Tele2, their coverage has surpassed even Telenor's according to latest network tests in 2021 but Telenor won the latest speed tests.
Telia Norge has confirmed that its 3G network has now been fully shut down – in line with plans announced back in 2018. With the operator having initially switched off its UMTS infrastructure in the Trondelag region and further south, it had retained 3G connectivity in more rural and remote regions to the north. Now, however, in a press release confirming the complete closure of its 3G network, the MNO noted that, having switched off its final 2100MHz 3G base station in June 2021, its last 900MHz 3G base station was confirmed as having been switched off November 2021.
Telia recently passed the milestone of 1000 5G sites in Norway as Ericsson continues to support the communications service provider in achieving nationwide 5G coverage by 2023.
The strategic partnership, which has already seen successful trials demonstrate the game-changing capabilities of 5G carrier aggregation, enables Telia Norway to be at the forefront of 5G and continue to set the bar high. The next goal is to add to the 1.5 million Norwegians who already have access to 5G and provide half of the country’s population with 5G coverage this year.
Multiple cities and municipalities around Norway have gained access to Telia’s 5G network since May 2020, when the Norwegian service provider’s first 5G network opened in Lillestrøm. Telia Norway’s subscribers with access to the network will be able to reap the benefits of higher speeds, increased capacity, and better coverage as eastern Norway becomes the next planned recipient of Ericsson and Telia’s 5G ambitions.
Norway’s Ice Group claims 10% market share
— Venture Capital News (@VC_News_UK) August 19, 2020
Ice Group , the third mobile operator in Norway, said it has captured a 10% share of the mobile market after five years of operation and is targeting a 20% market share in the medium term with the aim of https://t.co/d46FFJopAP pic.twitter.com/7fGs7LAj4s
Ice Group, is the third mobile operator in Norway, said it has captured a 10% share of the mobile market after five years of operation and is targeting a 20% market share in the medium term with the aim of reaching 25% in the long term.
Ice, which gained 4G spectrum in 2013 and acquired Network Norway from Telia in 2015, has been on a mission to break the longstanding duopoly of Telenor and Telia.
Ice had more success in Norway's first 5G auction in 2019, gaining 2x10MHz of 700MHz frequencies and 2x15MHz of 2.1GHz spectrum, spending NOK337 million ($38 million) in total. In May 2020, it then spent NOK1.58 million ($178,905) on new frequencies in the low 10GHz and 38GHz bands.
Ice has decided to accelerate its 5G rollout with the aim of reaching 75% population coverage, although without specifying a timeline. The operator currently has a national roaming agreement with Telia, and is also building their own mobile network. They have added 62 new smartphone base stations, bringing the total to 3,133. Ice has added 246 new smartphone base stations in 2021 to date, with a goal of between 300 and 500 for the year as a whole.
Related Posts:
- Operator Watch Blog: Nordics are Winning the Mobile Networks Experience Race
- Operator Watch Blog: Telenor Norway says 5G is the Key Enabler for Modernization going forward
- Operator Watch Blog: Ice - bringing 5G to Norway
- Operator Watch Blog: Telia 5G Strategy and Services
- Telecoms Infrastructure Blog: Telia Norway Launches 5G Fixed-Wireless Access (FWA)
- Operator Watch Blog - Telia: Largest Operator in Nordic & Baltic Region

No comments:
Post a Comment