For many years Oman’s mobile market was a duopoly between the incumbent telco Omantel and its challenger Ooredoo Oman. In February 2021, Vodafone Group and Oman Future Telecommunications consortium secured a license to operate the Sultanate’s third network, with services being under the Vodafone Oman brand.
Oman has a modern mobile sector which comprises substantial coverage of both 3G and LTE networks. In February 2021 Omantel launched commercial 5G services, while Ooredoo Group has a five-year framework agreement with Ericsson to develop its 5G platform across the Group’s ten markets, including Oman. The Covid-19 pandemic has caused a spike in mobile data traffic, which prompted Omantel to upgrade a number of sites from 3G to LTE, as well as build a number of additional 5G sites.
While Oman’s fixed broadband infrastructure penetration is considered low, it is being improved with the building of fibre-based networks as part of Oman’s Vision 2040 program.
Oman has also established itself as an important communications hub in the Middle East, with access to numerous submarine cables including the 2Africa submarine cable, which should become available during 2023-2024. The 9,800km Oman Australia Cable running from Muscat to Perth, with the potential for a branch line to Djibouti, is making progress and is expected to be completed in December 2021. This additional infrastructure will provide considerable additional bandwidth.
Regarding bands: 2G/GSM is on 900 MHz, 3G/UMTS on 900 and 2100 MHz. 4G/LTE started in 2013 on 1800 MHz (B3) on Omantel and Ooredoo and is available on prepaid. Ooredoo added 800 MHz for FD-LTE (B20) and Omantel started TD-LTE on 2300 MHz (B40) too.
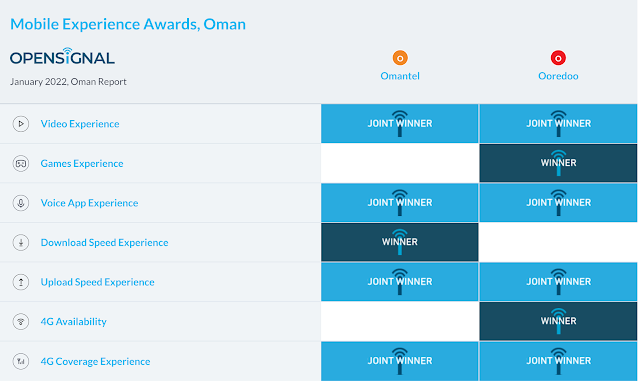
According to the recent Open Signal report (which only surveyed Ooredoo and Omantel), these two operators were joint winners in four out of seven categories due to statistical ties. Of the two, Ooredoo has the most outright wins, being the sole winner of both the Games Experience and 4G Availability awards, while Omantel is the outright winner of the Download Speed Experience award.
Omantel is the Sultanate’s incumbent telecoms operator and primary provider of internet in the country on landline and ADSL. It's mostly state-owned and market leader in mobile networks too. In 2018 it reached 56% of the market. It has the best coverage and speeds and most customers. It's mobile branch is also known as Oman Mobile. Its 4G/LTE reaches most populated areas.
In June 2021 Omantel and Ericsson announced the completion of a 5G millimetre wave (mmWave) proof of concept (PoC) trial that will enable the Omani operator to meet the increasing demand for high-quality connectivity as well as facilitate new use cases. When rolled out, 5G mmWave will greatly enhance the user experience at mobile broadband hotspots and home broadband (fixed wireless access [FWA]), as well as enable low-latency industry applications like Augmented Reality (AR). The trial delivered multi-gigabit speeds with eight cell carrier aggregation functionalities using Ericsson’s Streetmacro 6701 mmWave solution and advanced 5G software features. The trial used a carrier bandwidth of 800MHz at 26GHz, with 5G in Non-Standalone (NSA) mode of operation.
Omantel has also formed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) with the South Korean operator LG Uplus to expand its 5G offerings using edge technology. Included within the scope of the MoU is Augmented reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), Multiview, Timeslice solution and any potential business cooperation opportunities on XR platforms.
Ooredeoo is the 2nd provider in the country still giving good coverage in 3G and 4G: 3G 4G coverage maps. 3G covers 90% of the population and has reached 96% coverage of the Sultanate’s population with its ‘SuperNet’ 4G/LTE mobile network in 2019.
Ooredoo from Qatar has acquired the majority of the operator which was called Nawras before and renamed it to Ooredoo in 2014. It's the no.2 slightly behind Omantel at 46% share of the market in 2018. Generally Ooredoo has lower prices than Omantel at a slightly lower coverage.
In June 2021 Nokia and Ooredoo announced the introduction of super-fast and reliable 4G and 5G fixed wireless (FWA) access throughout Oman. Work to deploy the Nokia FastMile 4G FWA solution throughout the country commenced in February 2021. The scope of work initially saw 15,000 homes and businesses connected. In addition, 3,000 homes in city centers will soon get Nokia FastMile 5G FWA.
Vodafone has become the third operator in the sultanate. Vodafone Oman launched in January 2022. Their plans include bringing a next-generation 5G network and cloud services to Oman and then, its spokesperson said, moving into ecosystems that reach far beyond telecommunications.
Local reports suggest that the government initiated the bid for a new mobile operator to improve communication services, generate fresh job opportunities for Omanis, and enhance the country’s GDP. It’s not too surprising therefore that Vodafone Oman is highlighting a focus on employing Omanis and a local partnership ecosystem across key sectors. Vodafone will provide services through 3,500 authorized distributors and a comprehensive network.
The entry of a new player could also usher in some price competition, potentially benefiting consumers in a market where, according to some reports, internet access is seen as being high compared to other countries in the region. The country, whose population is around five million, is said to have nearly 1.2 million postpaid and 4.7 million prepaid mobile subscribers.
Vodafone received the licence to operate in Oman in 2019. Formal approval of Vodafone as the third operator was given a year ago.
Vodafone Oman also recently signed an agreement with Ericsson to deploy, operate and maintain a new 4G and 5G core and radio access (RAN) greenfield network.
Ericsson will supply a complete core network solution based on Ericsson Cloud Core, NFVI and Cloud VoLTE as well as an end-to-end transport network solution. The greenfield network includes other Ericsson Radio System products and solutions such as the antenna-integrated radio and Ericsson Spectrum Sharing. The end-to-end solution range will deliver a cost-efficient, energy-efficient, and flexible layered architecture design to support 5G from network launch. Vodafone customers will also benefit from Ericsson Voice over LTE (VoLTE) services.
Related Posts:
- Operator Watch Blog - Oman: On course for 5G

No comments:
Post a Comment